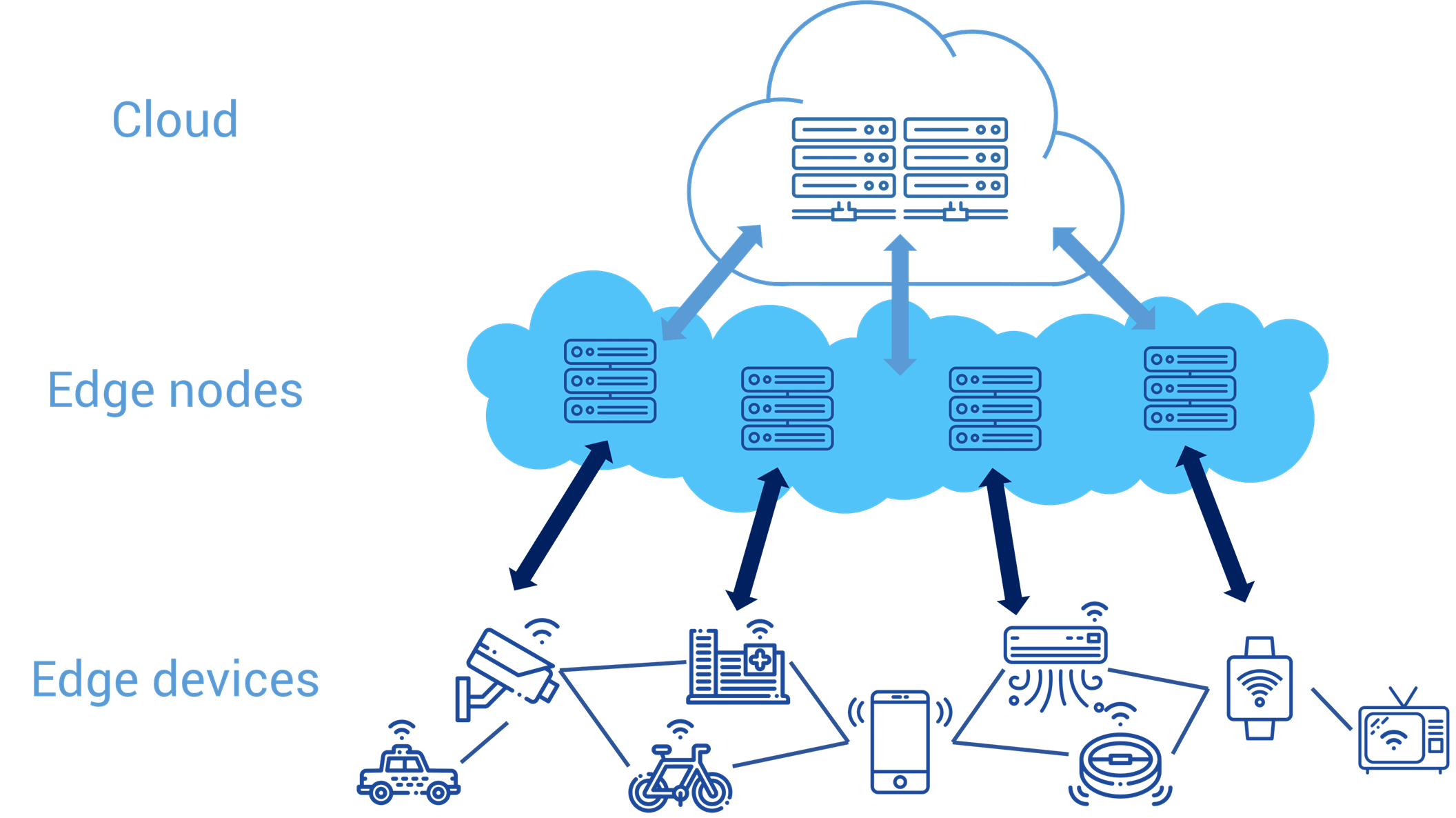
The cloud will continue to exist. Edge computing will provide compute power and storage in the space between the device and the cloud. Edge compute devices include IoT gateways, routers, and micro data centers in mobile network base stations.
Autonomous, local decision-making based on incoming IoT data and cached enterprise information. Distributed data management: which data to store, where and for how long.
Intelligence at the edge can help systems take decisions (routing) more quickly and efficiently. The opportunities come from technology evolving in manufactured devices and 5G networks, along with concepts, algorithms and standards in software-defined networking.
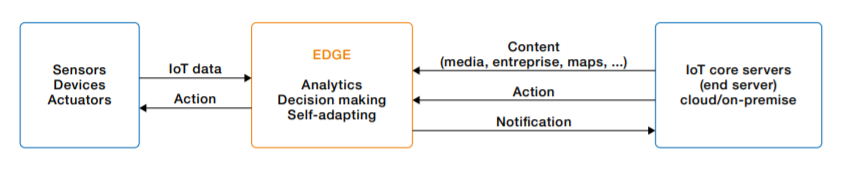
The IoT connects smartphones, tablets and almost anything with a sensor on it. These ‘things’ collect and exchange data, interact with business systems and create significant business outcomes. This radical transformation from the cloud to the edge will support trillions of systems and billions of systems.
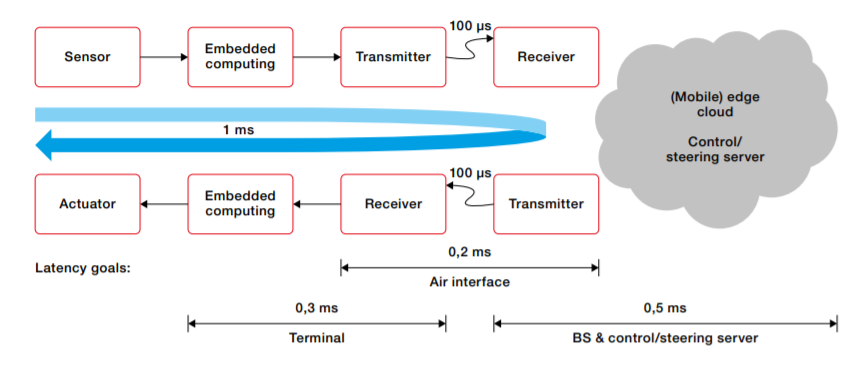
The capability to transmit data/touch in perceived real time is often referred to as the ‘tactile internet’ The latency requirements for the tactile internet are very challenging, with a round trip delay of 1 ms typically required. 5G promises to deliver ultra-low latency for a number of critical use cases, including industry automation, robotics and remote surgery. Deploying small cloudlets at the edge or very close to radio base stations can be useful for service-specific use cases. deploying a variety of cloud technologies can ensure scalable and low power computing support for tactile internet services. The evolution of computing models towards edge computing is described below.
Auto213