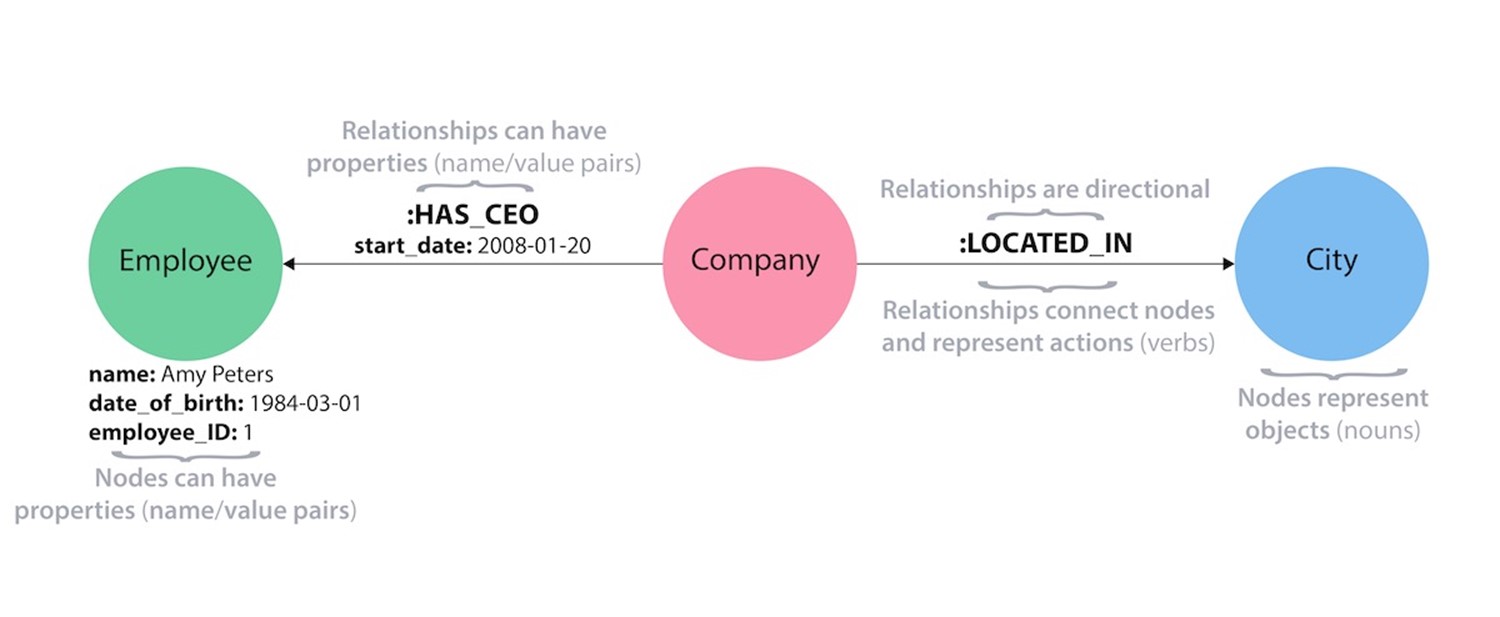
Abstract. In this paper, we develop a benchmark for graph database systems based on the real data of the Italian Business Register, consisting of about 10 million entities and 5 million relationships among them. We evaluate three state-of-the-art open source graph database systems – ArangoDB, Neo4J, and OrientDB – and we compare them to a well-known relational database management system, namely PostgreSQL. We found out that the strong points of graph databases are: the purposely designed storage techniques, which let them have good performance on graph datasets; and the purposely designed query languages, which go beyond the standard SQL and manage the typical problems that arise when graphs are explored. However, we have seen that the main performance increments have been obtained when heavy graph situations are queried; for simpler situations and queries, a relational database performs equally well.