‘Ethnic group’ is ‘a segment of a larger society whose members are thought, by themselves or others, to share important segments of a common culture’ ‘immigrant entrepreneurs’ would be an alternative term for ‘ethnic groups’. ‘Ethnic entrepreneurship’ refers to a set of connections and regular patterns of interaction among people.
Ethnic entrepreneurships include the individuals who have actually immigrated over the past few decades. This definition excludes, however, members of ethnic minority groups who have been living in the country for several centuries. ‘Ethnic’ on the contrary, does not exclude immigrant or minority groups.
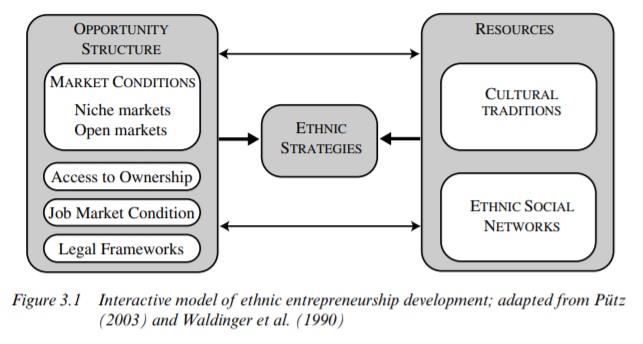
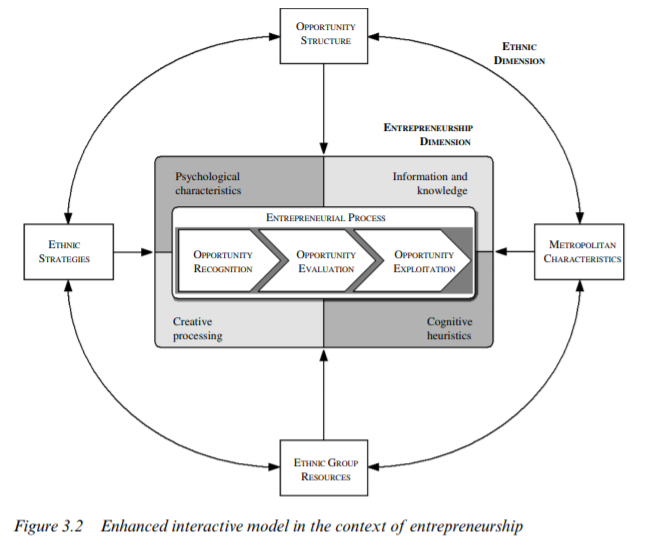
The authors believe that the ethnic-controlled economy permits fellow migrants to secure more and better jobs in the mainstream economy, reduce unemployment and improve working conditions. The ‘ethnic controlled’ economy is completely independent of the ‘ethnic ownership’ Economy.
Ethnic entrepreneurship is by no means a new phenomenon, as it is a firm part of any migration. An early and very prominent theory suggested that ethnic businesses are an obvious reaction to blocked opportunities in the labor market. In most cases, it was the ethnic community which created the demand for specific ethnic goods and services in the first place and which could only be fulfilled by co-ethnics with knowledge of tastes.
Cultural or structural factors influence the business entry decision and therefore are responsible for the rise of ethnic entrepreneurship. Supporters of the culturalist approach believe that immigrant groups have culturally determined features leading to a propensity to favor self-employment. The structuralist approach, on the other hand, suggests that external factors in the host environment, such as discrimination or entry barriers on the labor market due to education and language deficits, pushes foreigners into self- employment.
Auto323
Ethnic entrepreneurship: a theoretical framework