Business leaders across all industries and regions will increasingly be called upon to formulate a comprehensive workforce strategy. Policy-makers, educators, labor unions and individual workers likewise have much to gain from deeper understanding of the new labor market.
Global labor markets are set to undergo significant transformation over the coming five years. By 2022, the cluster of emerging professions is set to increase its share of employment from 16% to 27% of the total employee base of our company respondents. About half of today’s core jobs will remain somewhat stable in the period up to 2022.
The Future of Jobs Survey suggests a positive outlook for the future of jobs. Yet that outlook is underscored by a series of workforce shifts, set to accompany the adoption of new technologies. One of these indicates that 75 million jobs may be displaced by the above trends, while 133 million additional new roles may emerge concurrently. It should be noted that these projections primarily represent the share of roles within the remit of large multinational employers.
50% of companies expect that automation will lead to some reduction in their full-time workforce. 38% of businesses surveyed expect to extend their workforce to new productivity-enhancing roles. More than a quarter expect automation to lead to the creation of new roles in their enterprise. In addition, businesses are set to expand their use of contractors doing task-specialized work.
Across industries surveyed, jobs expected to become increasingly redundant over the 2018–2022 period are routine-based, middle-skilled white-collar roles. These shifts reflect unfolding and accelerating trends that have evolved over a number of recent years. Given that the skills requirements of emerging roles frequently look very different from those of roles experiencing redundancy, proactive, strategic and targeted efforts will be needed to map and incentivize workforce redeployment.
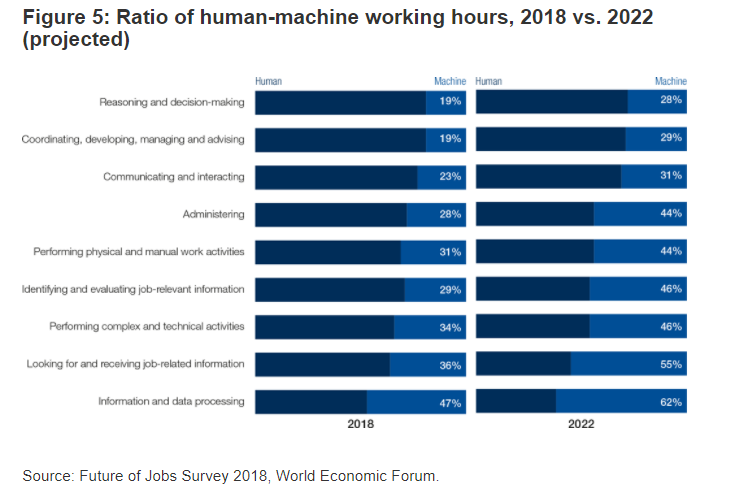
By 2022, this picture is projected to change somewhat, with machines and algorithms on average increasing their contribution to specific tasks by 57%. The expansion of machines’ share of work task performance is particularly marked in Reasoning and decision-making; Administering; and Looking for and receiving job-related information. optimally integrating humans and automation technology will require an analytical ability to deconstruct the work performed in their organizations today into discrete elements. For workers, improved productivity may allow them to re-focus their work on high-value activities that play to the distinctive strengths of being human.
2021auto22 reskill trends automation to augmentation
Workforce Trends and Strategies for the Fourth Industrial Revolution