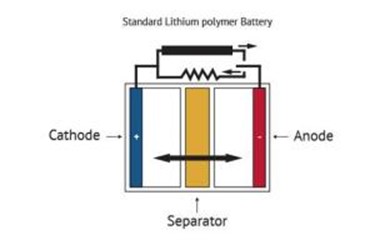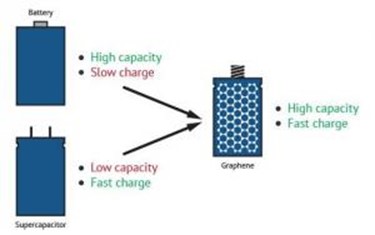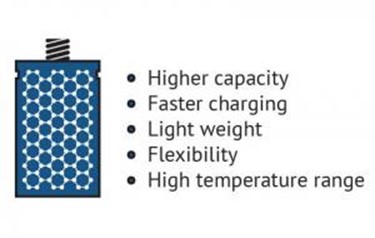
In the field of batteries, conventional battery electrode materials (and prospective ones) are significantly improved when enhanced with graphene. A graphene battery can be light, durable and suitable for high capacity energy storage, as well as shorten charging times. It will extend the battery’s life, which is negatively linked to the amount of carbon that is coated on the material or added to electrodes to achieve conductivity, and graphene adds conductivity without requiring the amounts of carbon that are used in conventional batteries.
Graphene can improve such battery attributes as energy density and form in various ways. Li-ion batteries (and other types of rechargeable batteries) can be enhanced by introducing graphene to the battery’s anode and capitalizing on the material’s conductivity and large surface area traits to achieve morphological optimization and performance.
It has also been discovered that creating hybrid materials can also be useful for achieving battery enhancement. A hybrid of Vanadium Oxide (VO2) and graphene, for example, can be used on Li-ion cathodes and grant quick charge and discharge as well as large charge cycle durability. In this case, VO2 offers high energy capacity but poor electrical conductivity, which can be solved by using graphene as a sort of a structural “backbone” on which to attach VO2 – creating a hybrid material that has both heightened capacity and excellent conductivity.