Industrial Ecology is a research field for holistically optimizing energy and resource efficiency. Industrial Ecology is an approach for the transition from a fossilfuel powered, linear economical system, to a more sustainable, circular, low-carbon economy. The SRG concept combines the idea of urban production and the ultra-efficient factory, with concepts of urban agriculture in the form of rooftop greenhouses. The Smart Rooftop Greenhouses Concept (SRG) is presented in a slightly extended version of the previous SRG paper. It aims to optimize the positive impacts of manufacturing on its surrounding environment.
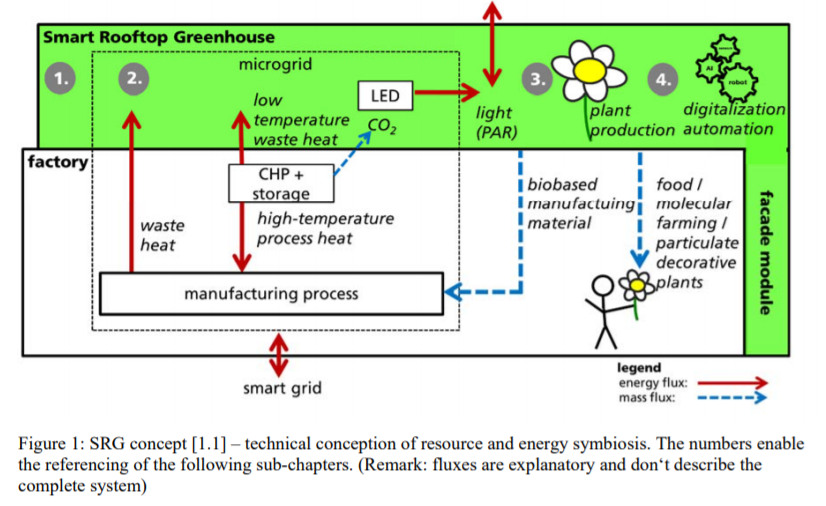
The SRG concept is an approach for the evolution of existing greenhouse technology into a digitalized and automated combination of industrial and biological production processes. The main subject matter of the concept is the energy symbioses of waste heat usage and smart grid integration to improve energy efficiency of a production system. The basic constructional element is the greenhouse (No. 1) on the rooftop and the facade of the factory. Through a modular design of the greenhouse, with different climate and lightning zones, the SRG can produce different species of plants. With the facade module, southwards facing facades can also be used for plant production.
The aim is to deliver energy flexibility to energy systems with a high share of variable renewable energy from wind and solar power. The energetic symbiosis of the SRG can be controlled and optimized by incorporating all energy generation, storage and consumption components into a micro-grid. The plant production in the greenhouse can deliver bio-based manufacturing material, food for the smart factory’s canteen and the consumers in the urban surrounding areas. Another market for highest-value plant-production can be the pharmaceutical industry. Decorative plants, e.g. for indoor offices, is another potential market.
Farm5
Urban Production: Smart Rooftop Greenhouses as a Technology for Industrial Energy Symbiosis