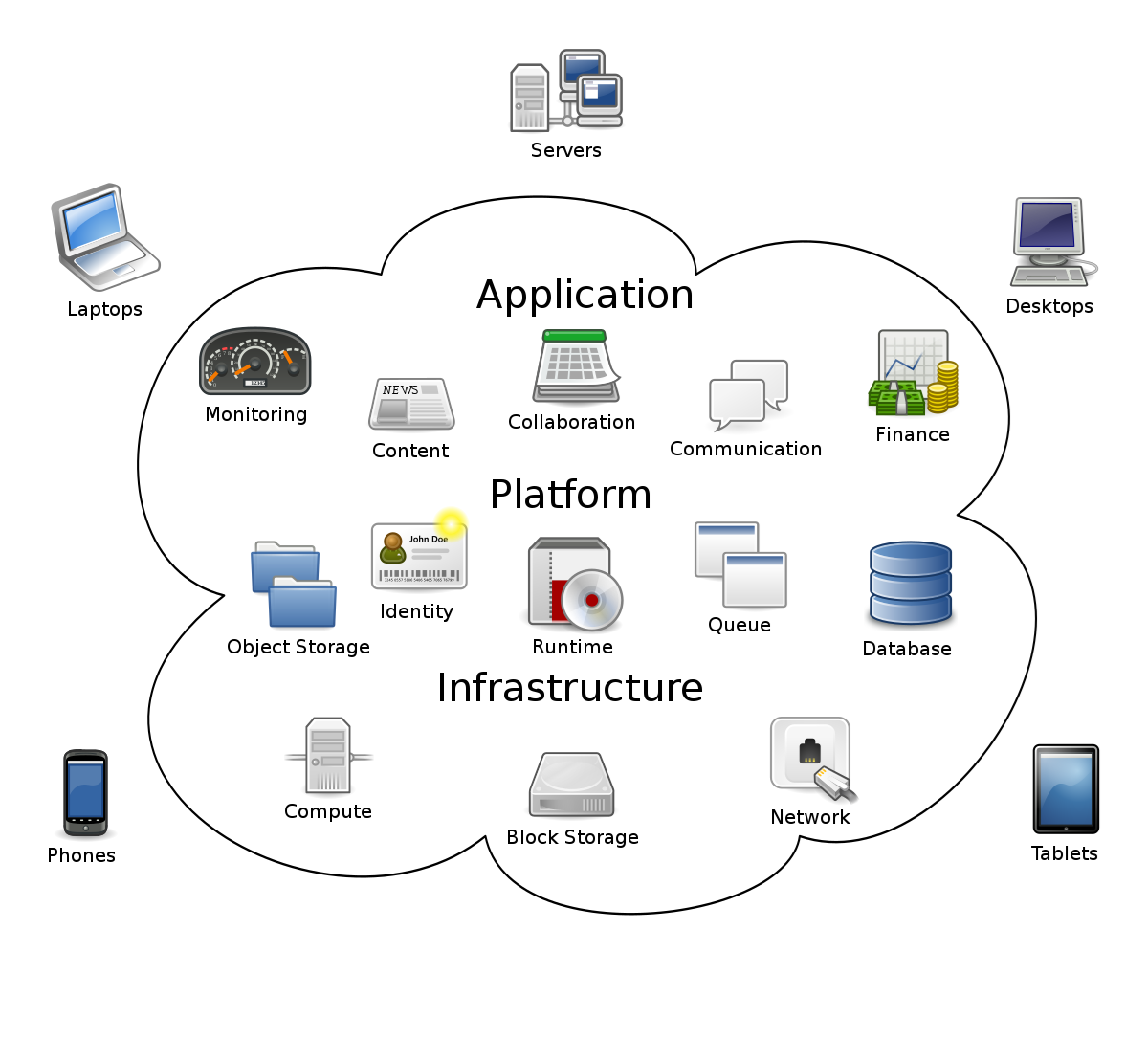
There may be no single, accepted definition of cloud computing. Some view it narrowly as virtual server access and use that is contracted from a third party. The third party cloud or “hosting” provider maintains the hardware, software and updates on the server. This contractual arrangement sometimes provides smaller, and sometimes larger, companies with a higher level of IT support than the companies can afford to hire as their own staff. The cloud provider focuses on a more narrow scope of IT service and spreads the cost of professionals over all the companies that contract to use their hosting services.
With Gmail, the email software and the actual mail both reside on Google’s servers in the “cloud.” No copy of the email is maintained on your computer. The fact that the software and data reside in the cloud and not on company computers can sometimes save a significant amount of costs. If we apply this concept to business and accounting software, an accounting system usually existed on the company’s computers and the data was also stored there. The company need not have the accounting software and data within the company. Employees can access the accounting software through a Web browser.
Third-party providers of cloud-based services are called cloud service providers (CSPs) CSPs can provide a range of services, including hosting, maintenance, and data storage. CSP’s can also provide software as a service (SaaS) or as an operating system (OS) for the cloud service provider to use. The CSP can provide cloud services for as long as a year, or as little as a few months, depending on the needs of the service provider. The service provider can charge a fee for the use of the CSP, which can be in the form of a monthly fee.
The major difference between cloud computing and client–server computing is where the software and data reside. Accounting software that is sold today is generally categorized into market segments, described in the next section. The company’s system is accessed via the cloud, which in some cases is operated by the software company and in other cases by a third party software hosting firm.
Auto273